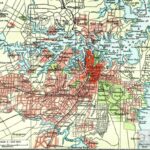
The Sydney Zone

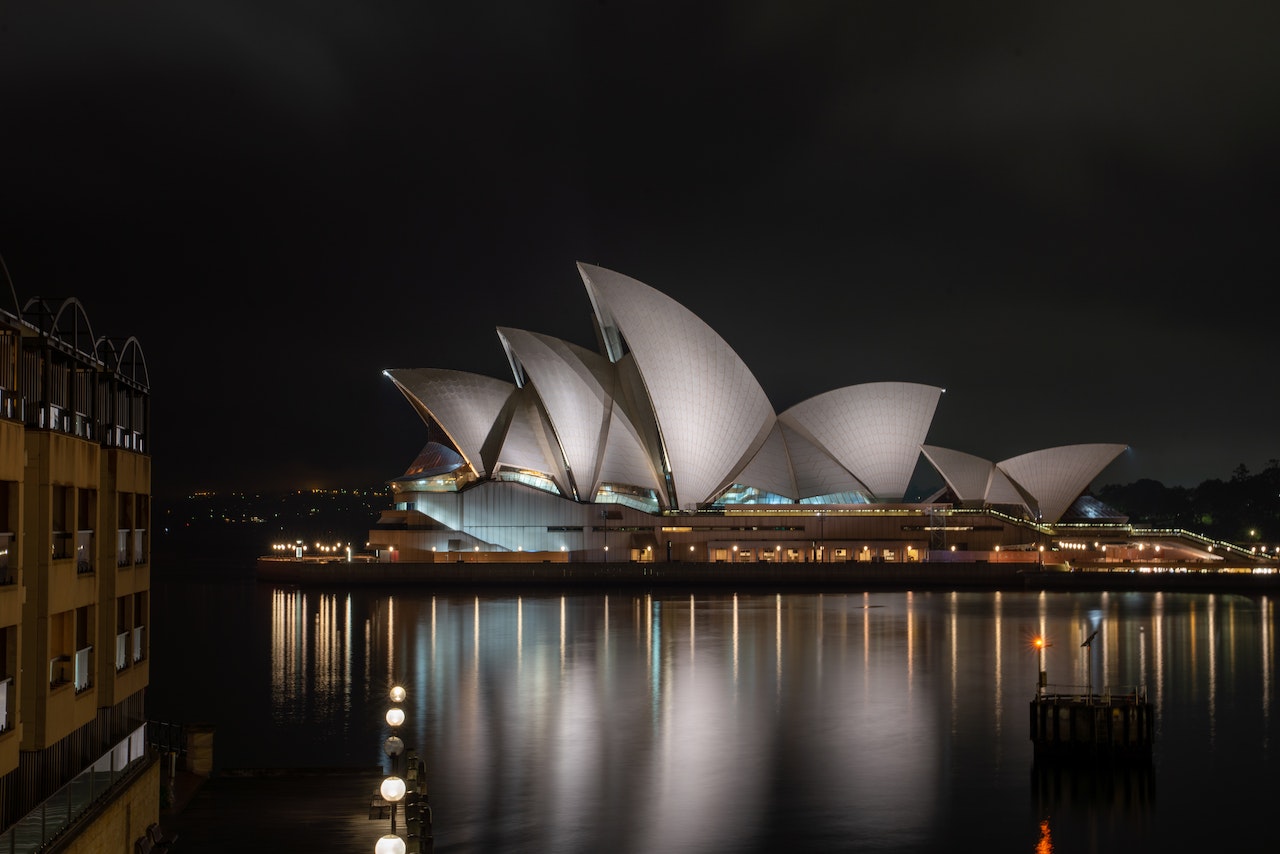
Sydney at Night
Sydney is a large metropolitan area, typically divided into different regions that frequently correspond with suburbs, local government areas or cadastral units.
As New South Wales struggles to meet its homebuilding target, a new NSW government plan targets several train stations in Sydney’s outer suburbs for high density housing projects. But this plan has drawn criticism from several councils and communities.
Location
Sydney is a major commercial, cultural and tourist center located on Australia’s southeastern coast. Home to numerous parks and attractions like the Sydney Opera House and Royal Botanic Garden.
Sydney is considered a warm temperate city. It experiences dry summers with high temperatures and low humidity levels; winters range from cool to cold with occasional frost formation; rainfall levels remain moderate with peak precipitation occurring around spring time.
There are two official weather stations in Sydney’s metro area, Observatory Hill and Kingsford Smith Airport. Generally speaking, Sydney’s Lower North Shore comprises areas between Lane Cove River and Middle Harbour including Boundary Street Roseville through Mosman Council areas, Hornsby Shire areas to Westleigh Pennant Hills Road on Pennant Hills Road; it may also encompass parts of Ku-ring-gai Municipality. Conversely, Upper North Shore refers to those between M1 Motorway Wahroonga and M2 Motorway Chatswood respectively.
Climate
Sydney, known for being one of the world’s most livable cities, attracts travelers seeking an inviting balance of warmth and cool all year long. Winter temperatures tend to be mild while in summer the heat may be broken by an occasional southernerly breeze bringing cold fronts.
Sydney can be classified as having a subtropical climate (Koppen climate classification: Cfa), with warm to hot summers and mild winters; its proximity to the ocean reduces extreme seasonal differences.
Fog is a common sight during winter mornings, particularly during June when moist easterlies prevail. Suburban areas tend to experience radiation fog as a result of night-time cooling by land or water sources nearby, particularly when rain and cloudiness is higher than usual; streamflows also tend to exceed average during this season – specifically those flowing into Hawkesbury-Nepean and Shoalhaven rivers which serve Sydney but their flow can be altered due to diversions for consumptive use.
Population
Sydney is Australia’s largest city and, according to the Economist Intelligence Unit, ranks fourth as one of the world’s most liveable places. Stability, health care access, culture and education all play a part in making Sydney one of the four most liveable places.
Zoning restrictions have led to the creation of what are known as satellite cities; suburban areas that have expanded outside zone boundaries due to cheaper land prices and ease of transport, creating upward trends in office and retail development beyond central business district limits.
In 2021, over one quarter of residents living in the City of Sydney local area worked in professional and business services while nearly one fifth worked in construction. Roman Catholics were by far the largest religious group within this population segment followed by Anglicans and Eastern Orthodox Christians; other religions made up smaller percentages. Furthermore, one-third were foreign born residents with India, China, and Britain representing over 50%.
Economy
Sydney is Australia’s financial, commercial, shipping and industrial capital. Its economy largely comprises services with jobs available in government, finance, commerce, retailing and transport – as well as entertainment education tourism and manufacturing including oil refining.
City services include numerous airports, a major seaport and an extensive network of railways, roads and freeways. Due to its geographical position in one of the world’s great harbors and its diverse culture, its workforce has proven highly flexible.
Greater Western Sydney is Australia’s third-largest economic zone, accounting for 8% of GDP and home to one out of every 11 Australians. Its rise as an economic powerhouse can be attributed to several factors: an expanding and increasingly sophisticated local economy; improved job access opportunities and dedication to innovative infrastructure development projects. Greater Western Sydney strives to realise its vision of being a 30-minute city where residents live, work and play within 30 minutes from jobs, services and great places.